Furthering the prostate cancer screening debate (prostate cancer specific mortality and associated risks).
Abstract
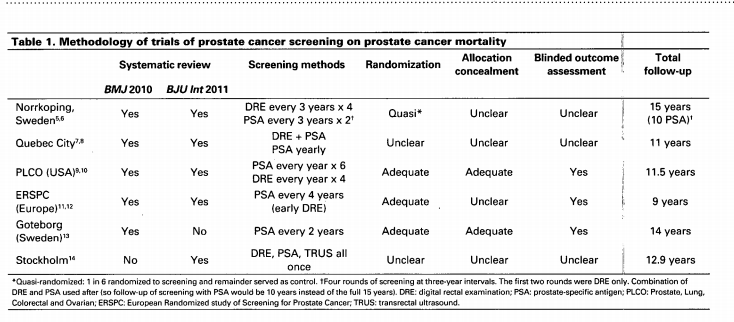
Screening for prostate cancer remains a contentious issue. As with other cancer screening programs, a key feature of the debate is verification of cancer–specific mortality reductions. Unfortunately the present evidence, two systematic reviews and six randomized controlled trials, have reported conflicting results. Furthermore, half of the studies are poor quality and the evidence is clouded by key weaknesses, including poor adherence to screening in the intervention arm or high rates of screening in the control arm. In high quality studies of prostate cancer screening (particularly prostate–specific antigen), in which actual compliance was anticipated in the study design, there is good evidence that prostate cancer mortality is reduced. The numbers needed to screen are at least as good as those of mammography for breast cancer and fecal occult blood testing for colorectal cancer. However, the risks associated with prostate cancer screening are considerable and must be weighed against the advantage of reduced cancer–specific mortality. Adverse events include 70% rate of false positives, important risks associated with prostate biopsy, and the serious consequences of prostate cancer treatment. The best evidence demonstrates prostate cancer screening will reduce prostate cancer mortality. It is time for the debate to move beyond this issue, and begin a well-informed discussion on the remaining complex issues associated with prostate cancer screening and appropriate management.