Identification of Hepatotropic Viruses from Plasma Using Deep Sequencing: A Next Generation Diagnostic Tool
PLoS One. 2013 Apr 17;8(4):e60595. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060595. Print 2013.
Law J1, Jovel J, Patterson J, Ford G, O’keefe S, Wang W, Meng B, Song D, Zhang Y, Tian Z, Wasilenko ST, Rahbari M, Mitchell T, Jordan T, Carpenter E, Mason AL, Wong GK.
Abstract
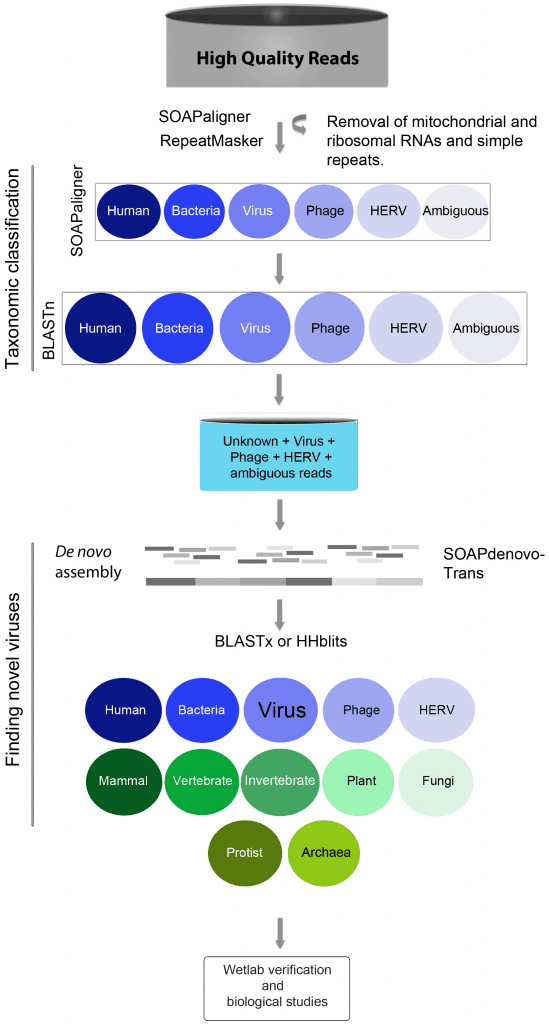
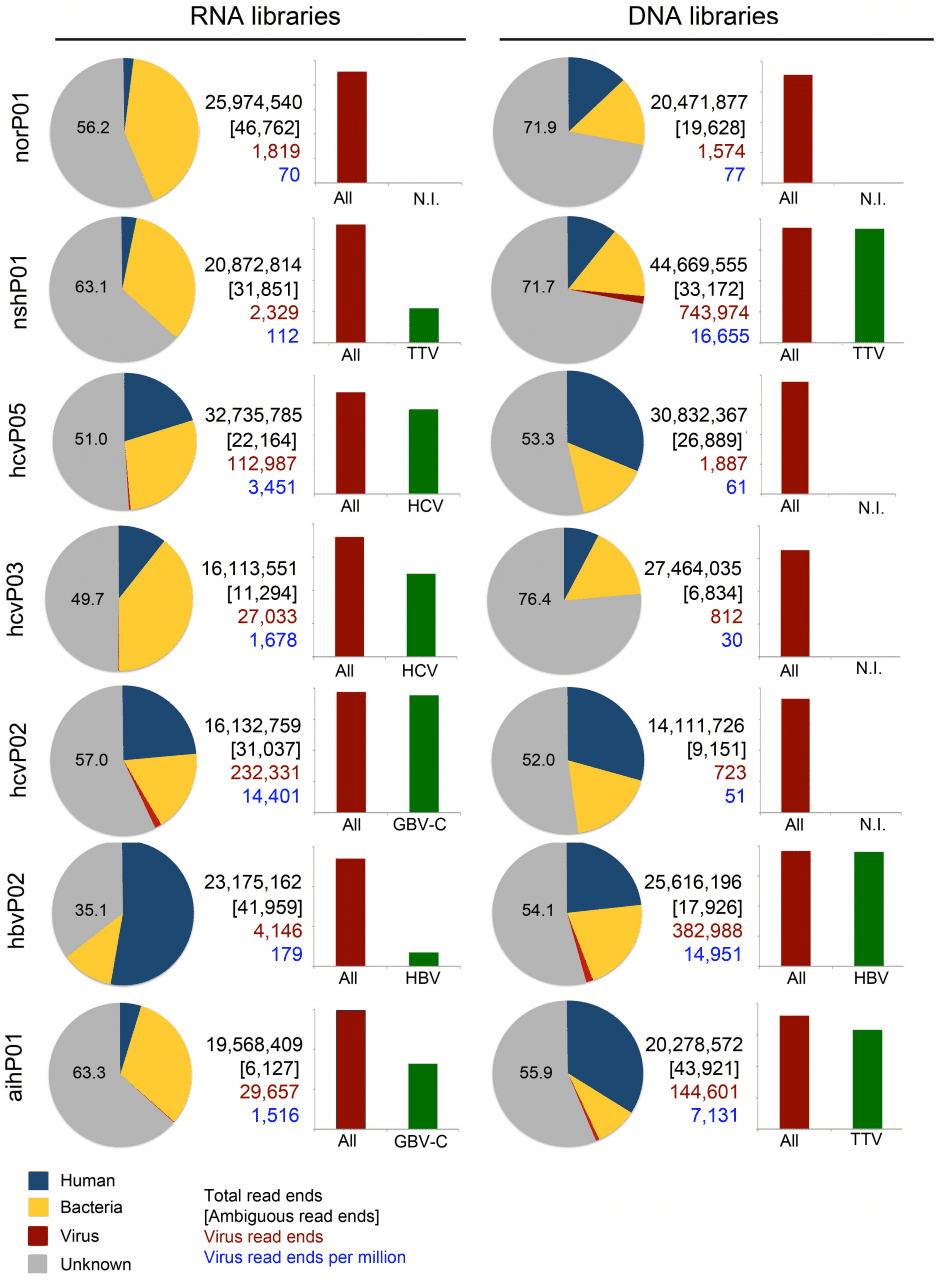
We conducted an unbiased metagenomics survey using plasma from patients with chronic hepatitis B, chronic hepatitis C, autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), and patients without liver disease (control). RNA and DNA libraries were sequenced from plasma filtrates enriched in viral particles to catalog virus populations. Hepatitis viruses were readily detected at high coverage in patients with chronic viral hepatitis B and C, but only a limited number of sequences resembling other viruses were found. The exception was a library from a patient diagnosed with hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection that contained multiple sequences matching GB virus C (GBV-C). Abundant GBV-C reads were also found in plasma from patients with AIH, whereas Torque teno virus (TTV) was found at high frequency in samples from patients with AIH and NASH. After taxonomic classification of sequences by BLASTn, a substantial fraction in each library, ranging from 35% to 76%, remained unclassified. These unknown sequences were assembled into scaffolds along with virus, phage and endogenous retrovirus sequences and then analyzed by BLASTx against the non-redundant protein database. Nearly the full genome of a heretofore-unknown circovirus was assembled and many scaffolds that encoded proteins with similarity to plant, insect and mammalian viruses. The presence of this novel circovirus was confirmed by PCR. BLASTx also identified many polypeptides resembling nucleo-cytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV) proteins. We re-evaluated these alignments with a profile hidden Markov method, HHblits, and observed inconsistencies in the target proteins reported by the different algorithms. This suggests that sequence alignments are insufficient to identify NCLDV proteins, especially when these alignments are only to small portions of the target protein. Nevertheless, we have now established a reliable protocol for the identification of viruses in plasma that can also be adapted to other patient samples such as urine, bile, saliva and other body fluids.