Enhanced Detection of Cancer Biomarkers in Blood-Borne Extracellular Vesicles Using Nanodroplets and Focused Ultrasound
Cancer Res. 2017 Jan 1;77(1):3-1
Paproski RJ, Jovel J, Wong GK, Lewis JD, Zemp RJ.
Abstract
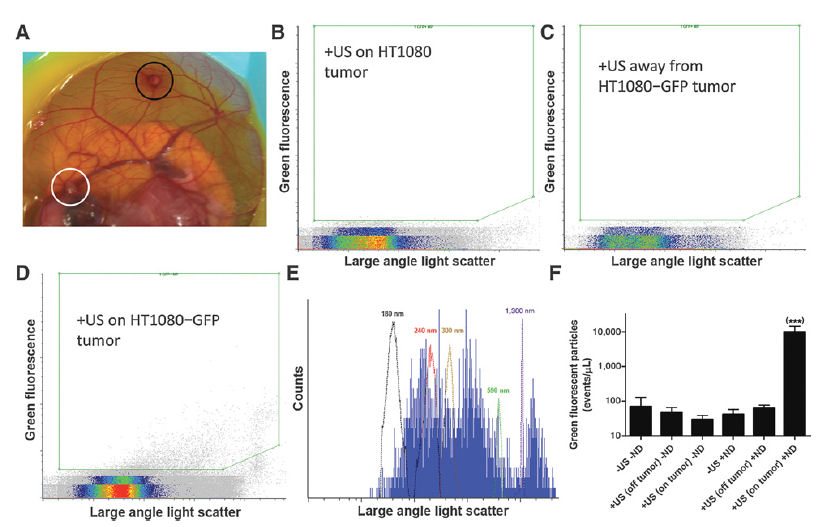
The feasibility of personalized medicine approaches will be greatly improved by the development of noninvasive methods to interrogate tumor biology. Extracellular vesicles shed by solid tumors into the bloodstream have been under recent investigation as a source of tumor-derived biomarkers such as proteins and nucleic acids. We report here an approach using submicrometer perfluorobutane nanodroplets and focused ultrasound to enhance the release of extracellular vesicles from specific locations in tumors into the blood. The released extracellular vesicles were enumerated and characterized using micro flow cytometry. Only in the presence of nanodroplets could ultrasound release appreciable levels of tumor-derived vesicles into the blood. Sonication of HT1080-GFP tumors did not increase the number of circulating tumor cells or the metastatic burden in the tumor-bearing embryos. A variety of biological molecules were successfully detected in tumor-derived extracellular vesicles, including cancer-associated proteins, mRNAs, and miRNAs. Sonication of xenograft HT1080 fibrosarcoma tumors released extracellular vesicles that contained detectable RAC1 mRNA with the highly tumorigenic N92I mutation known to exist in HT1080 cells. Deep sequencing serum samples of embryos with sonicated tumors allowed the identification of an additional 13 known heterozygous mutations in HT1080 cells. Applying ultrasound to HT1080 tumors increased tumor-derived DNA in the serum by two orders of magnitude. This work is the first demonstration of enhanced extracellular vesicle release by ultrasound stimulation and suggests that nanodroplets/ultrasound offers promise for genetic profiling of tumor phenotype and aggressiveness by stimulating the release of extracellular vesicles.